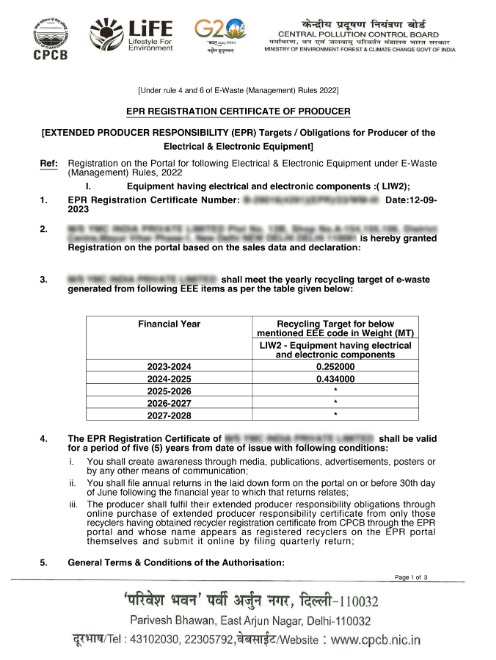
E-Waste Registration for EPR
What does EPR mean for e-waste?
As part of Extended Producer Responsibility (EPR), companies that make, import, or own brands of electrical and electronic equipment (EEE) are responsible for collecting, recycling, refurbishing, and safely getting rid of their own electronic goods when they become useless. This makes sure that dangerous materials from old electronics don't end up polluting the earth.
E-waste, or electronic waste, refers to discarded electrical and electronic equipment such as computers, mobiles, TVs, batteries, refrigerators, and other gadgets.
With the rapid growth of technology, India has become one of the largest producers of e-waste in the world. To control this growing problem, the Government of India introduced the E-Waste (Management) Rules, 2016, later updated in 2022, under the Environment (Protection) Act, 1986. A major part of this system is the E-Waste Registration, which ensures that producers, recyclers, and refurbishers handle e-waste responsibly and legally.
The E-Waste (Management) Rules, 2022 say that companies that sell electronic goods must have EPR Registration from the Central Pollution Control Board (CPCB), keep their certificates up to current, and meet their annual recycling goals.
ask@makemerchant.com
+91 7011192293